DAkkS eAttestation signatures
Memida now offers an extended feature for inspection reports that validates PDF, XML, and DCC (digital calibration certificate) files for DAkkS-compliant eAttestation signatures.
An eAttestation is a machine-readable, cryptographically secured electronic confirmation introduced by DAkkS. It combines a digital seal with the digital DAkkS accreditation symbol and allows real-time machine and human verification. This makes it possible to prove the origin and integrity of digital documents—similar to a digital signature from an accredited body. Learn more on the DAkkS website.
New features at a glance
Automatic validation in inspection reports
Memida now automatically checks every inspection report to see whether PDF, XML, or DCC documents contain a valid DAkkS eAttestation signature, ensuring compliance with DAkkS guidelines.
Clear status display
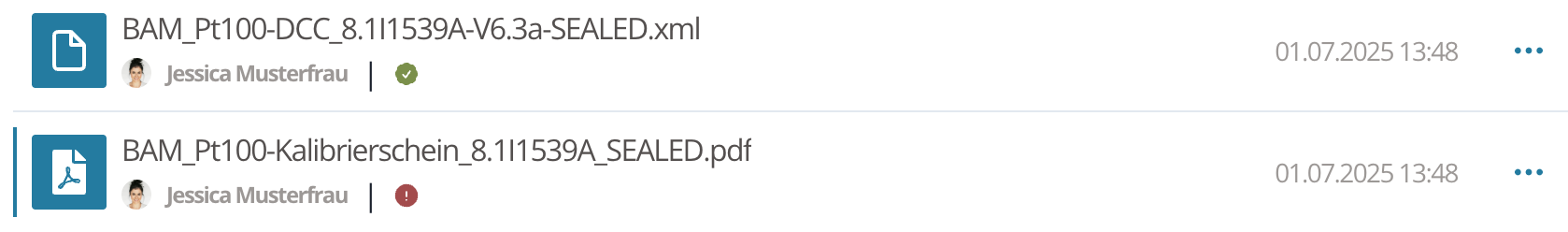
The validation results are displayed clearly:
- A success message appears when the signature is valid.
- If validation fails, the affected check step is listed in detail.
Status messages only appear for documents that contain a digital accreditation symbol.
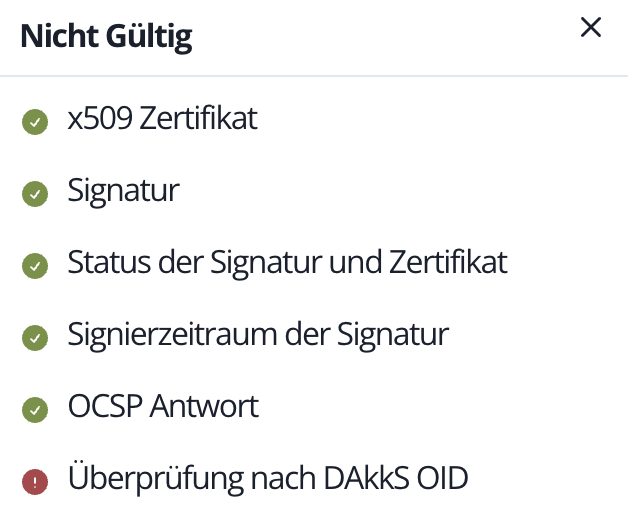
Transparency for error messages
If validation fails, the affected steps are shown to help you analyze and fix issues quickly.
Memida follows these DAkkS TSPS validation steps:
- Step 1 (Signature check): Verify the cryptographic integrity of the certificate.
- Step 2 (Validity period): Ensure the certificate is still within its validity period.
- Step 3 (Revocation status): Check the certificate via OCSP or CRL.
- Step 4 (Certification path validation): Confirm that the certification path to the trust anchor (root CA) is valid.
- Step 5 (Digital official emblem): Validate the structure and details of the digital accreditation symbol in the certificate.
General improvements
Additional bug fixes and optimizations further improve the stability and performance of Memida.
